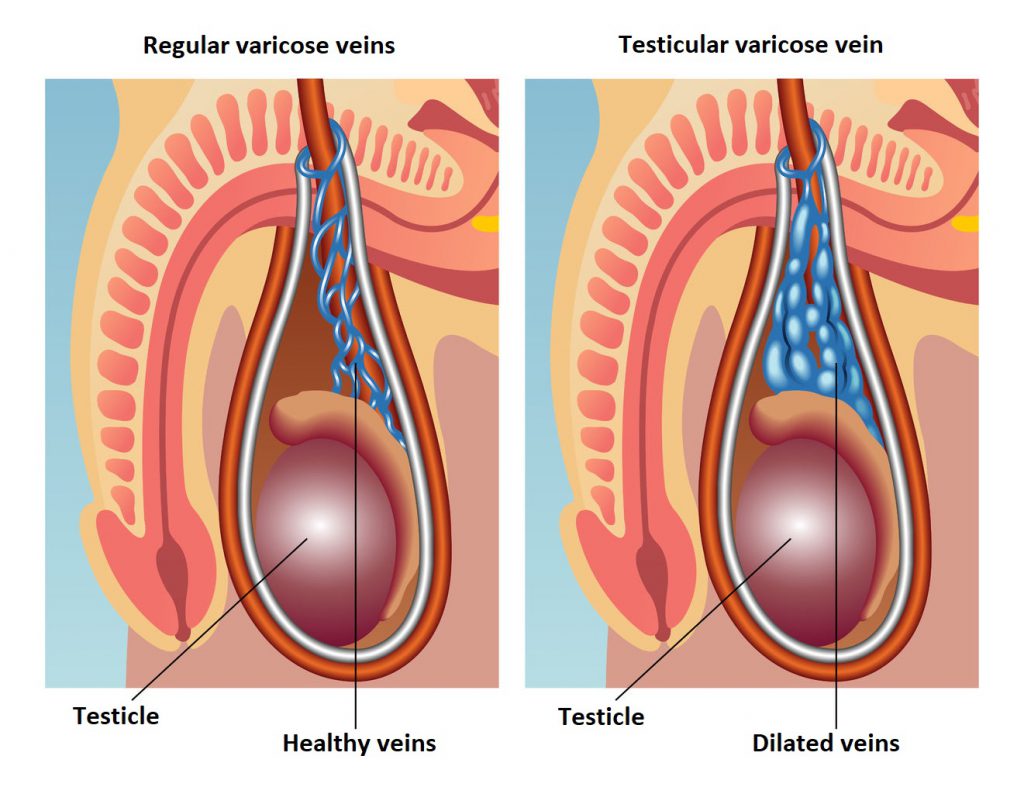
Varicocele

Varicocele treatment
Testicular surgery can be performed in several basic ways:
Open surgery: This is the most common method, in which the testicle is reached through an incision in the abdomen or groin. The surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia, and during the surgery we need a microscope and Doppler in order to reduce as much as possible the possibility of complications. The recovery process after surgery is fast, and the pain caused by this process is minimal.
Laparoscopic varicocele surgery: In this surgery, a small incision is made by inserting a small camera and another incision to insert the surgical equipment. And this surgery is rarely performed because it is associated with anesthesia and with more complications than open surgery.
Percutaneous embolization: a radiologist intervenes in this surgery, and during this operation, a catheter is inserted into the veins, so that we see on the radiograph that the catheter is in a place, where we can release small stents to block the vein expander; This surgical method is not widely followed because it is more complex than other methods and has greater complications.
If the varicocele causes slight discomfort and does not need surgery, regular pain relievers can be used to relieve pain. In addition, elastic underwear can be used, which supports the testicle and reduces congestion in the veins.
The most important complications associated with varicocele are:
Shrinkage of the testicle: The bulk of the testicle consists of a series of tubes that produce sperm cells. These tubes are exposed to damage and therefore the production of sperm cells is damaged, which leads to testicular shrinkage. One of the explanations for this condition is the accumulation of blood in the testicles. This leads to a greater effect of toxic substances, which leads to cell death.
A decrease that may lead to infertility: The main objective of the network of veins in the testicle is to cool the testicle and prevent its temperature from rising, as the ideal temperature for the work of testicular cells is 35 ° C, so the testicles are located in the scrotum outside the body and the temperature is likely to rise Testicle when blood flow in the testicle becomes slower than normal due to the varicocele, which will limit the movement of sperm cells.
Undescended testicle:
The treating doctor can determine if one of the testicles has not descended into its place in the scrotum, and he can perform tests to locate the testicle to determine the changes that occur in its place. The doctor may recommend surgery for the undescended testicle, where the doctor gently and softly pulls the hanging testicle towards the scrotum
Hydrocele of the testicle:
It is a swelling in the scrotum caused by the accumulation of fluid in the thin tissue surrounding the testicles. It most commonly affects newborns and usually disappears without treatment within a year of birth. The injury is usually the result of an infection or injury to the scrotum, which does not cause pain and does not usually require treatment unless the scrotum is swollen and in the case of sudden or severe pain in the scrotum. In this case, you should see a doctor, as surgery may be needed. It could be a sign of another condition called testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a condition in which the testicle feels like squeezing, usually as a result of an injury or accident.
Male circumcision surgeries:
A surgical procedure in which the thin skin covering the front part of the penis, which is also called the “foreskin”, is removed. It is preferable to perform this surgery within 24 to 72 hours of birth by a specialist doctor, and it can also be performed late after birth, but in That condition becomes more serious. It is a once in a lifetime process.
Boy circumcision date:
40 days after birth.
It differs from one child to another in the shape and length of the skin, as well as in the method of circumcision.
There are modern methods for this process, which are
• Excision by thermal cautery or scalpel (surgery)
Thermal cautery device or scalpel is used to perform male circumcision surgery and cut the excess skin. The thermal cautery device is the best, because it works on thermal cauterization of blood vessels, to avoid the child from bleeding.
• Plastic bell circumcision.
It is a sterile plastic ring in the shape of a bell, which is inserted between the cat of skin to be removed and the penis, according to the size of the diameter of the penis of the child, and after taking the appropriate size for the front piece of skin that covers the head of the penis “the foreskin”, the piece of skin is pulled back And tie it firmly with the thread until atrophy occurs in the last part of the skin to be cut, and it continues inside the penis of the child for about a week until the ring falls off with the part of the skin attached to the thread.

The plastic ring has many benefits that include:
Ensure that the child does not bleed.
Not using surgical sutures.
Extremely safe for children with hemophilia, due to the closure of the blood vessels with the thread attached to the ring.
It gives a cosmetic shape, as the skin is even on all sides.
The disadvantages of traditional methods are fading, as the possibility of re-circumcision of the child is reduced again.
It can be performed on the first day of birth, unless the baby has a birth defect.
