What are breast surgeries?
They are operations that target to eradicate breast tumors and the masses in it, which is to remove the tumor, whether it is benign or malignant from the breast. This type of operation is considered a preservative surgery, as surgery allows us to preserve the shape of the breast by removing the tumor. Breast cancer surgery may be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy.
This operation is done to eradicate the benign or malignant tumor as soon as the tumor is discovered, where the tumor is removed from the breast, provided that this tumor has not penetrated the tissue boundaries, because this condition is what guarantees the eradication of the tumor completely, without removing the breast itself.
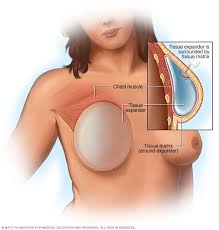
The goal of breast cancer surgery is to remove cancerous cells from the breast, and these operations are considered relatively recent, because in the past, the entire breast was removed in all cases in which a tumor was diagnosed in the breast, which left the sick woman with a lot of medical and psychological repercussions.
What happens during this process of breast lumpectomy, is that a sample is taken from the sentinel node, which is the lymph node responsible for draining the breast through the armpit in order to make sure that there are no hidden cancer cells in the lymphatic tract.
Here we will review the most important information about breast surgery and breast tumors and their symptoms.
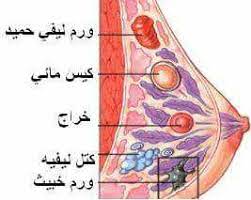
There are several symptoms of breast cancer:
• The appearance of a lump in the breast or under the armpit.
• A change in the shape or the size of the breast
• A Change in the shape or the color of the nipple: scaly, limp, retraction, secretions change in the shape of the skin of the breast: bump, scaling, the shape of an orange peel….and unusual pain.
• A change in the shape or the size of the breast
• A Change in the shape or the color of the nipple: scaly, limp, retraction, secretions change in the shape of the skin of the breast: bump, scaling, the shape of an orange peel….and unusual pain.
Types of breast cancer surgery:
• Surgery to remove the entire breast (mastectomy)
A total mastectomy is a surgery to remove all of the breast tissue. It’s most often done by making a cut (incision) on the chest, but it can be done in different ways.
• A Surgery to remove a part of the breast tissue (lumpectomy)
• A Surgery to remove nearby lymph nodes.
• A Surgery to reconstruct the breast after it has been completely removed.
Determining the most appropriate type depends on several factors, such as:
-The size of the cancer
– Cancer stage
Situations for which breast cancer surgery is necessary:
• High risk of developing breast cancer.
• Cases that have a strong family history of the disease.
• Identified non-cancerous breast biopsy results or a genetic mutation in a prophylactic (preventive) mastectomy with or without immediate breast reconstruction as an option to prevent breast cancer.
Risks of performing the operation Having a mastectomy is associated with many risks, such as the following:
• Infection of the incision site.
• Bleeding.
• Scars at the incision site.
• A drop in blood pressure.
• The death of some tissues as a result of problems in supplying them with blood.
• Fluid accumulation in the arm.
• A Surgery to remove a part of the breast tissue (lumpectomy)
• A Surgery to remove nearby lymph nodes.
• A Surgery to reconstruct the breast after it has been completely removed.
Determining the most appropriate type depends on several factors, such as:
-The size of the cancer
– Cancer stage
Situations for which breast cancer surgery is necessary:
• High risk of developing breast cancer.
• Cases that have a strong family history of the disease.
• Identified non-cancerous breast biopsy results or a genetic mutation in a prophylactic (preventive) mastectomy with or without immediate breast reconstruction as an option to prevent breast cancer.
Risks of performing the operation Having a mastectomy is associated with many risks, such as the following:
• Infection of the incision site.
• Bleeding.
• Scars at the incision site.
• A drop in blood pressure.
• The death of some tissues as a result of problems in supplying them with blood.
• Fluid accumulation in the arm.
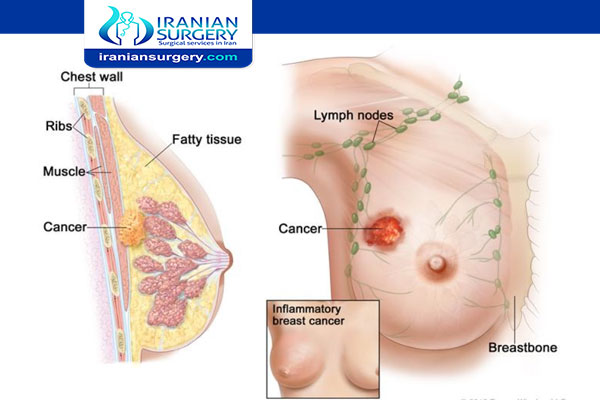
There are procedures that must occur before the operation:
• Some tests should be performed as needed, such as: blood tests, complete blood cell count, blood chemistry, coagulation tests, and chest x-rays, especially in the elderly, and an electrocardiogram is done.
• A biopsy is taken from the breast to diagnose the type of tumor, and in some cases other tests are performed, such as: computerized tomography, positron emission tomography, mammography, or breast ultrasound.
• Medications that are stopped before the operation are determined for 48 hours and fasting for 8 hours before the operation.
• A biopsy is taken from the breast to diagnose the type of tumor, and in some cases other tests are performed, such as: computerized tomography, positron emission tomography, mammography, or breast ultrasound.
• Medications that are stopped before the operation are determined for 48 hours and fasting for 8 hours before the operation.
The procedures that are performed during breast cancer surgery:
Sentinel Node sampling; to make sure that there are no hidden cancer cells in the lymphatic tract.
• Sterilization of the chest area completely, then the surgeon makes an incision in the lower border of the tumor.
• Removing the entire tumor from the healthy breast tissue by making an incision in the breast to remove the cancer and the surrounding tissue. The amount of tissue removed depends on whether you’re having a lumpectomy, to remove part of your breast tissue, or a mastectomy, to remove all of your breast tissue. The position and length of the incision depends on the location of the cancer within the breast.
• Excision and examination of some of the healthy breast tissue surrounding the tumor; to make sure that it is free of any cancer cells.
• Suture the healthy breast tissue again after making sure that it is free of any tumors.
• The operation to remove breast tumors takes from one to two hours, and some tubes are left to drain fluids from the tissues.
• Evaluate the lymph nodes under your armpit. During a sentinel node biopsy, the surgeon removes a few lymph nodes into which the tumor is most likely to drain first (the sentinel nodes). It is then screened for cancer. If no cancer is present, no additional lymph nodes need to be removed.
• If cancer is found, the surgeon may remove more lymph nodes or recommend radiation therapy to the lymph nodes after surgery. Sometimes both lymph node treatments are combined.
• Closing the incision the surgeon closes the incision in a cosmetic way that preserves your appearance. Dissolvable stitches are placed to reduce scarring.
After the surgery, you can expect to:
• The patient must stay in the hospital under observation for 24 hours after the operation to remove the lump from the breast to ensure the stability of the condition.
• After that, they are transferred to the recovery room, where blood pressure, pulse and breathing are monitored.
• There is a dressing (a bandage) over the surgical area.
• You may feel pain, numbness and pinching under the arm
• Get instructions on how to take care of yourself at home, including taking care of fissures and drains, recognizing signs of infection, and understanding activity limitations.
• Talk to your health care team about when to start wearing a bra or a breast prosthesis
• You will be given prescriptions for pain-relieving medicines and possibly an antibiotic, and the recovery period may reach a full week, and it is preferable during this period to get enough rest.
• Go to the doctor directly if some symptoms appear, such as: severe pain, high temperature, shortness of breath, purulent secretions, and severe bleeding.
breast abscess
A breast abscess is formed as a result of the breast tissue being exposed to a microbe that penetrates when the breast is cracked or scratched, which leads to severe inflammation that causes the pus to collect in a focus within the breast tissue.
• Sterilization of the chest area completely, then the surgeon makes an incision in the lower border of the tumor.
• Removing the entire tumor from the healthy breast tissue by making an incision in the breast to remove the cancer and the surrounding tissue. The amount of tissue removed depends on whether you’re having a lumpectomy, to remove part of your breast tissue, or a mastectomy, to remove all of your breast tissue. The position and length of the incision depends on the location of the cancer within the breast.
• Excision and examination of some of the healthy breast tissue surrounding the tumor; to make sure that it is free of any cancer cells.
• Suture the healthy breast tissue again after making sure that it is free of any tumors.
• The operation to remove breast tumors takes from one to two hours, and some tubes are left to drain fluids from the tissues.
• Evaluate the lymph nodes under your armpit. During a sentinel node biopsy, the surgeon removes a few lymph nodes into which the tumor is most likely to drain first (the sentinel nodes). It is then screened for cancer. If no cancer is present, no additional lymph nodes need to be removed.
• If cancer is found, the surgeon may remove more lymph nodes or recommend radiation therapy to the lymph nodes after surgery. Sometimes both lymph node treatments are combined.
• Closing the incision the surgeon closes the incision in a cosmetic way that preserves your appearance. Dissolvable stitches are placed to reduce scarring.
After the surgery, you can expect to:
• The patient must stay in the hospital under observation for 24 hours after the operation to remove the lump from the breast to ensure the stability of the condition.
• After that, they are transferred to the recovery room, where blood pressure, pulse and breathing are monitored.
• There is a dressing (a bandage) over the surgical area.
• You may feel pain, numbness and pinching under the arm
• Get instructions on how to take care of yourself at home, including taking care of fissures and drains, recognizing signs of infection, and understanding activity limitations.
• Talk to your health care team about when to start wearing a bra or a breast prosthesis
• You will be given prescriptions for pain-relieving medicines and possibly an antibiotic, and the recovery period may reach a full week, and it is preferable during this period to get enough rest.
• Go to the doctor directly if some symptoms appear, such as: severe pain, high temperature, shortness of breath, purulent secretions, and severe bleeding.
breast abscess
A breast abscess is formed as a result of the breast tissue being exposed to a microbe that penetrates when the breast is cracked or scratched, which leads to severe inflammation that causes the pus to collect in a focus within the breast tissue.
As for its symptoms:
• Marked swelling and pain in the breast.
• Severe pain at the site of the injury.
• Desire for itching and redness of the breasts.
• High temperature of the breast.
• Sensation of a lump with a hard border like a cyst. However, in most cases, the abscess is fixed and immobile.
There are factors that increase the risk of breast abscess, including:
• Breastfeeding.
• Weakened immunity.
• Diabetes.
• Severe pain at the site of the injury.
• Desire for itching and redness of the breasts.
• High temperature of the breast.
• Sensation of a lump with a hard border like a cyst. However, in most cases, the abscess is fixed and immobile.
There are factors that increase the risk of breast abscess, including:
• Breastfeeding.
• Weakened immunity.
• Diabetes.
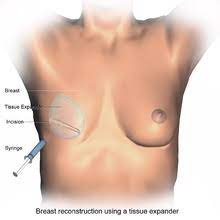
As for the treatment of breast abscess:
In most cases of large and advanced breast abscesses, treatment requires surgical opening of the abscess, through a simple surgical operation performed under complete anesthesia, and during this technique an incision is made in the breast to open, wash and clean the abscess.
With regard to small internal abscesses, it is possible to resort to withdrawing the contents of the abscess by the needle, which is accompanied by obtaining accurate and regular treatment with antibiotics, and this case must be followed up to repeat the withdrawal, when necessary, until the abscess is completely healed.
Full recovery after breast abscess removal usually takes one or two weeks, which is the period needed for the symptoms of acute inflammation such as pain and redness to end.
The treatment of breast abscess depends on the cause of its occurrence. If the infection was caused by milk retention, the doctor may advise the use of a milk inflator that eliminates this retention.
An antibiotic is prescribed to kill the abscess-causing bacteria.
There are some ways to relieve the symptoms of an abscess until it ends, including:
• Using warm compresses on the abscess area to reduce swelling and swelling of the breast, relieve pain and speed up treatment of the problem.
• Continue to breastfeed the child.
There are several ways to prevent a breast abscess:
• Maintaining the cleanliness of the breast in order to protect it from any bacterial infection that could infect it.
• Enhancing the health of the immune system by taking care of eating healthy foods that enhance the functions of the immune system, such as: fruits, vegetables, and protein.
• Regular breastfeeding, because it plays a major role in avoiding breast abscess, because it prevents milk from being retained inside.
• Periodic breast examination because it helps to discover any health problem that affects it early, through examining the breast by looking at it and start pressuring on its various parts.
There are some ways to relieve the symptoms of an abscess until it ends, including:
• Using warm compresses on the abscess area to reduce swelling and swelling of the breast, relieve pain and speed up treatment of the problem.
• Continue to breastfeed the child.
There are several ways to prevent a breast abscess:
• Maintaining the cleanliness of the breast in order to protect it from any bacterial infection that could infect it.
• Enhancing the health of the immune system by taking care of eating healthy foods that enhance the functions of the immune system, such as: fruits, vegetables, and protein.
• Regular breastfeeding, because it plays a major role in avoiding breast abscess, because it prevents milk from being retained inside.
• Periodic breast examination because it helps to discover any health problem that affects it early, through examining the breast by looking at it and start pressuring on its various parts.
